2.13 Industrial Access
Industrial Access Streets are adjacent to industrial and manufacturing land uses. They are designed to accommodate significant volumes of large vehicles such as single unit trucks, tractor trailers, and other delivery vehicles.
Intelligent Transportation Systems
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) facilitate dynamic transportation operations and include traffic signals. Read More »
Protected Bike Lanes
Object separated bike lanes are built at the same level as the surface of the street. Separation from traffic or parking is thus provided entirely by a painted median and a physical separation element (e.g. curb, planter, flex delineators). Read More »
3.11 Freight
Industrial Access streets are designed for significant volumes of large vehicles such as trucks, tractor trailers, and other delivery vehicles. The focus is on function. Read More »
3.9 Intersections
Sufficient curb radius on Industrial Streets is important for designing for truck turning movements. Read More »
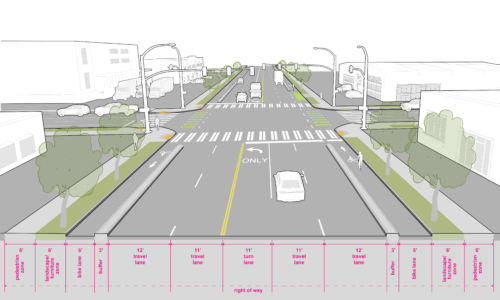
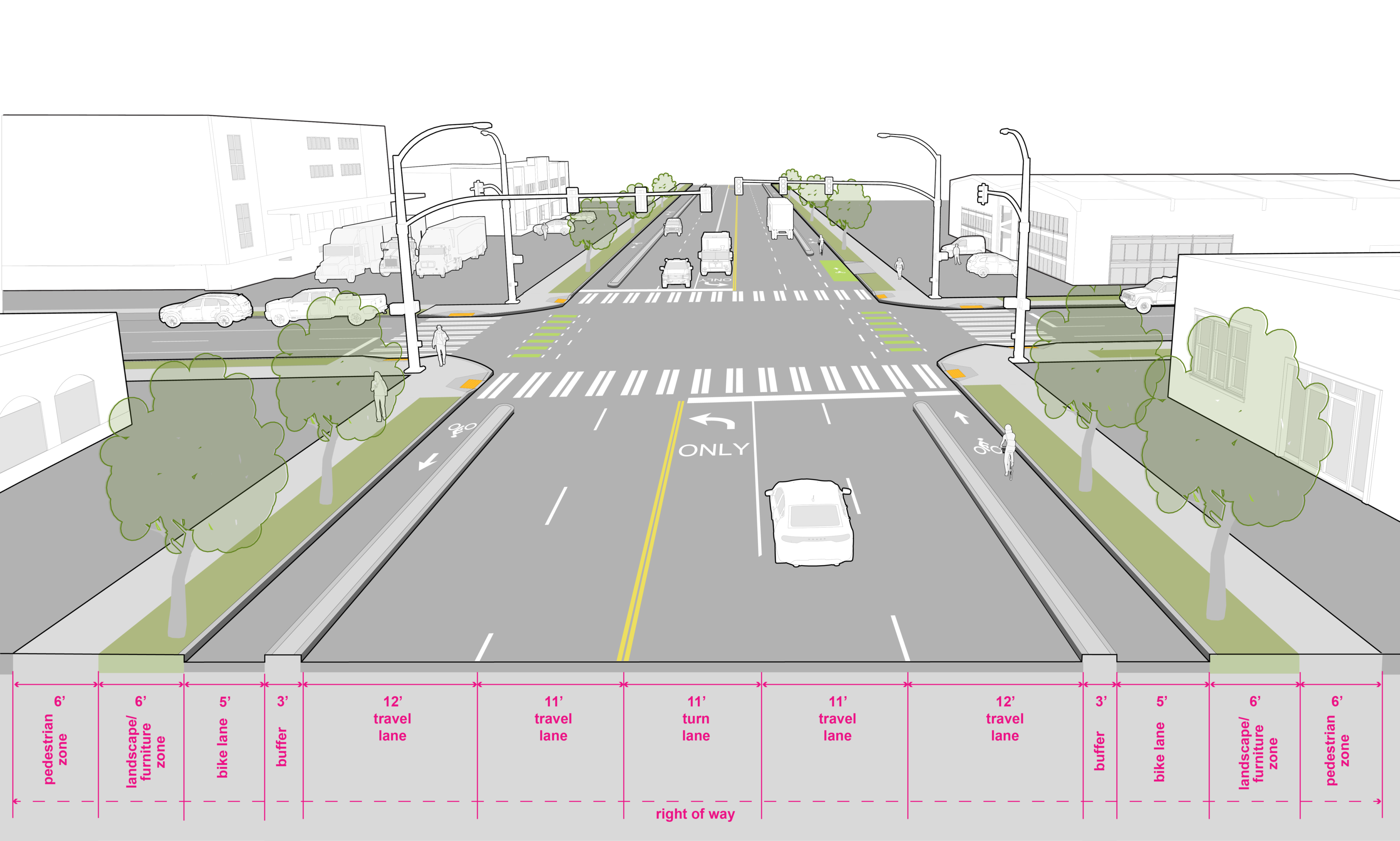
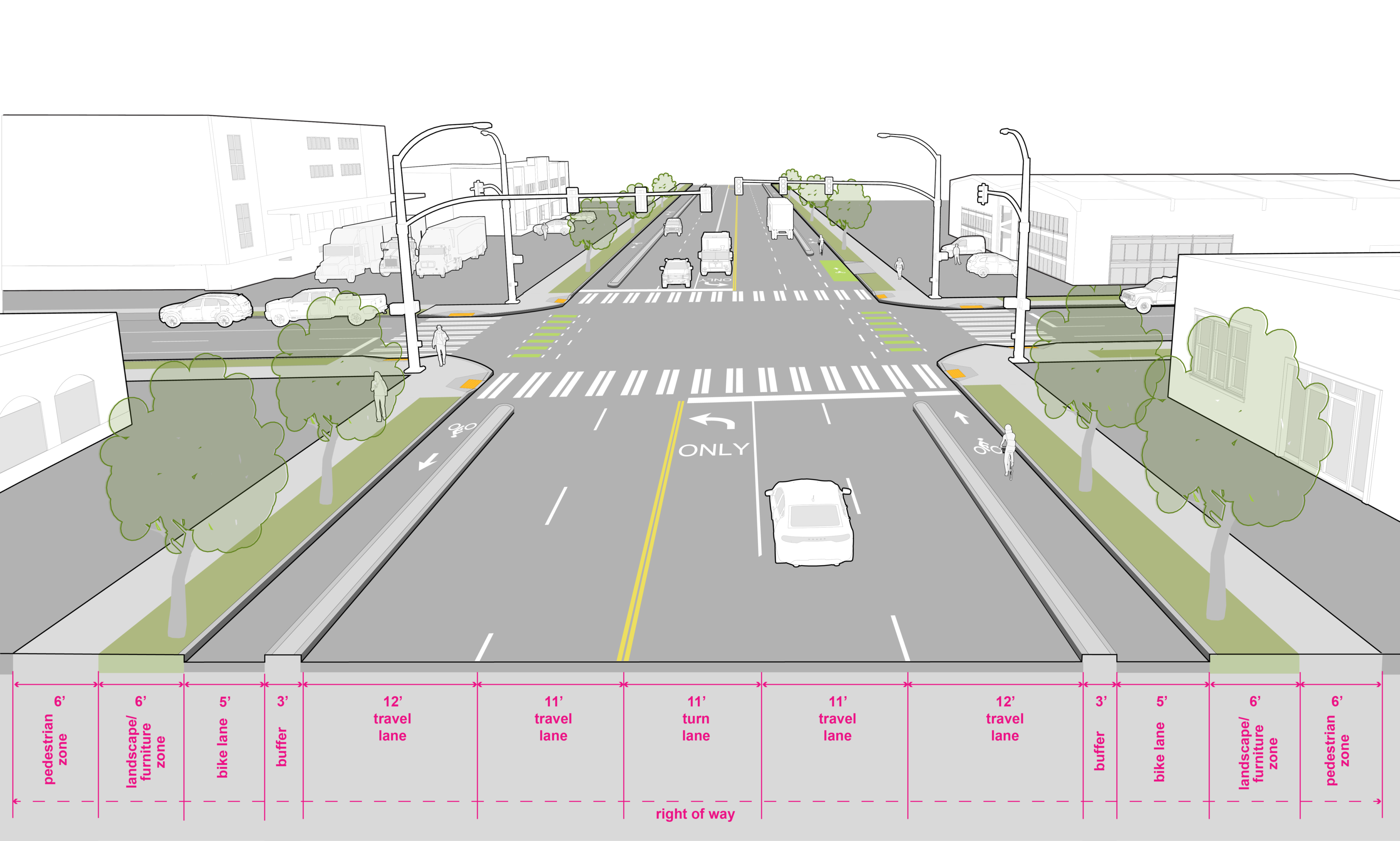
Industrial Access Streets, serving as connections to regional transportation facilities are designed for large vehicle turning maneuvers into and out of industrial properties. This street type may provide opportunities for temporary parking of trucks or staging of equipment or other materials associated with industrial uses. If a bicycle facility has been recommended in the bicycle master plan on an industrial access street, parking and other curb space demands from the adjacent industrial land uses must be taken into consideration.
|
Typical Street Classification(s) |
|
|
Public Space Programming |
|
|
Greening |
Street trees, permeable pavement or bioretention for sidewalks, landscaping, rain gardens. |
|
Pedestrian |
The pedestrian zone should be 6′ wide. Curb cuts and driveways should be limited, see Seattle Land Use Code Section F for more information on number of curb cuts permitted for street frontage of the lot. At intersections on streets with three or more travel lanes, signals are required to accommodate pedestrian crossing. |
|
Bicycle |
Protected bike facilities should be factored into the cross section when there are BMP recommendations. Bicycle facilities on Industrial Access Streets should provide physical separation to encourage proper positioning of bicyclists and vehicles, which improves visibility and predictability while providing a higher level of comfort for bicyclists. |
|
Freight |
This street type is designed to serve the freight network. Curb radii requirement is 30′ to serve larger vehicles, such as the WB50 and WB67. |
|
Transit |
Limited transit service due to nature of land use in the Industrial Centers. |
|
Curb Lane/Flex Zone |
Parking requirements should be provided on private property and/or accessed by alley. Consider a 9′ flex zone when sufficient right of way exists. |
*Color for illustration is used to differentiate between right-of-way elements and does not represent standard color for design.