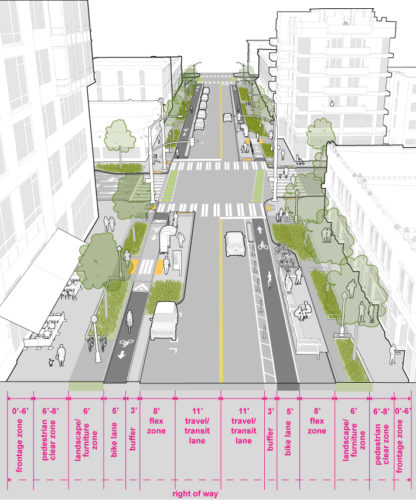
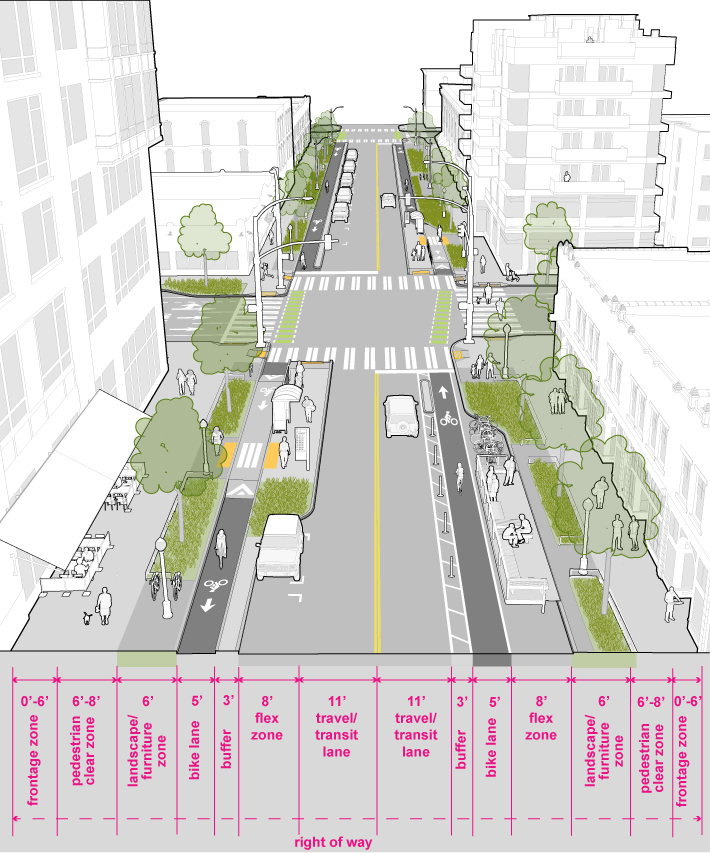
2.6 Downtown Neighborhood
Downtown Neighborhood Streets serve a more diverse variety of land uses and are typically smaller in scale than Downtown Streets.
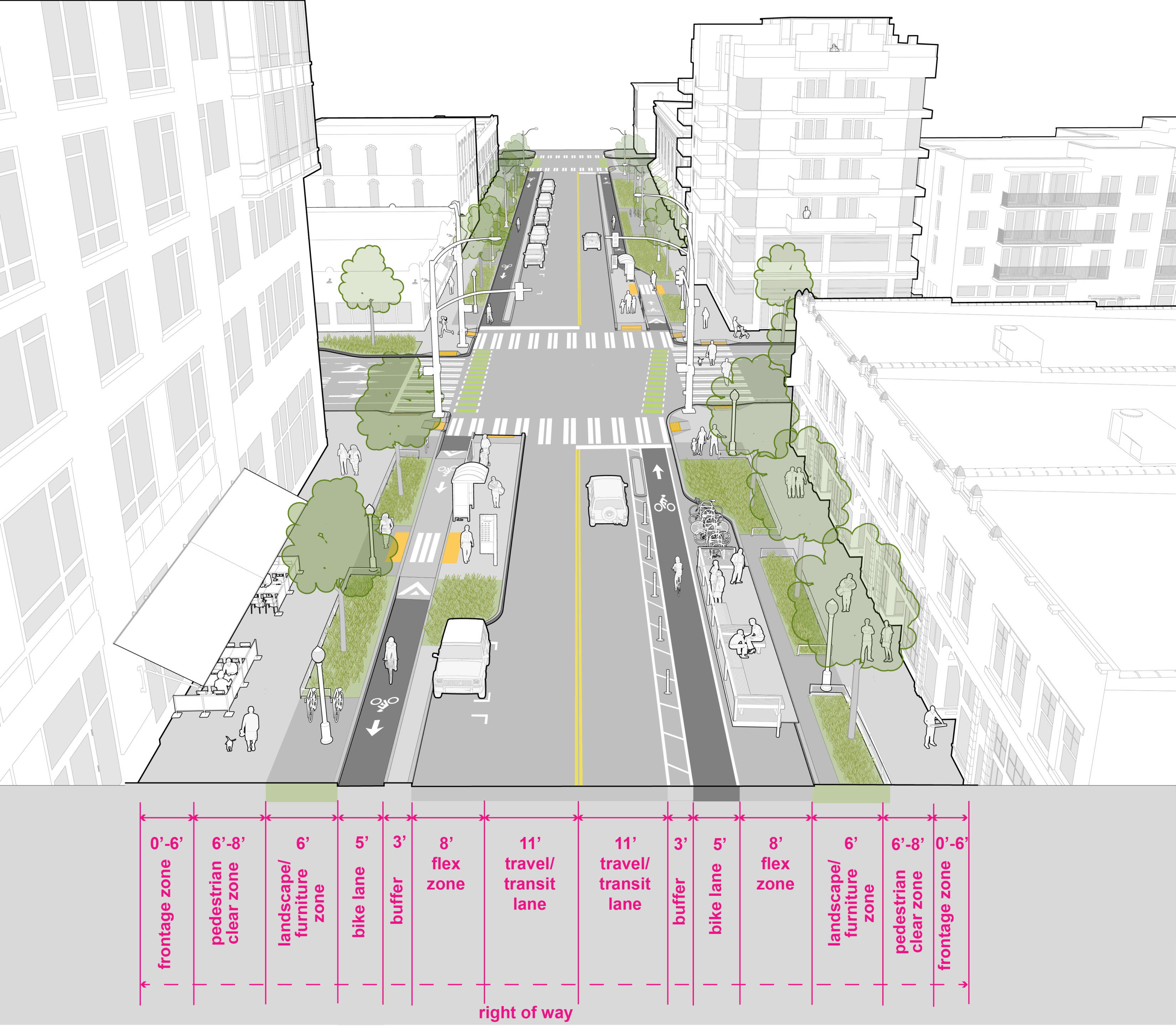
Bike Lanes and Transit Service
Where bike lanes are located along the same side of the street as transit, conflicts should be minimized and efficiency maximized between bicyclists and transit vehicles. Read More »
Intersection Treatments
Crossing treatments may be included at intersections to keep pedestrians, motorists, and cyclists safe. Read More »
Bike Parking
On-street (short-term) bike parking may be provided in the form of corrals or clusters of inverted U racks. The SDOT bicycle rack program website provides information on requesting a bike corral. Read More »
Parklets
Public space, landscaping, street furniture, parklets, and street cafes contribute to an intimate, neighborhood-oriented streetscape. Read More »
3.6 Street and Pedestrian Lighting
Street and pedestrian lighting can facilitate movement and visibility and improve safety for pedestrians and vehicles. Read More »
They are found in downtown districts such as Belltown and Pioneer Square, these streets support a lively mix of retail, residential, office and entertainment uses. These streets support high levels of walking, bicycling as well as frequent parking turnover, including loading zones. Downtown Neighborhood Streets accommodate public spaces, landscaping and other elements that contribute to a more pedestrian-friendly, neighborhood-oriented streetscape. Transit may also be present. Sidewalk width is dictated by the Seattle Land Use Code on many downtown streets. See Map 1 C in SMC 23.49 for specific sidewalk width requirements.
|
Typical Street Classification(s) |
|
|
Public Space Programming |
Sidewalk cafes, Parklets, Streateries, public plaza activation (special activities permit), Vending, Festival Streets, Bike Parking, Public Art. |
|
Greening |
Street trees, permeable pavement for sidewalks, landscaping, rain gardens, sloped or walled bioretention cells (pursuant to vertical wall policy). See Downtown Design Standards for landscaping standards. |
|
Pedestrian |
Medium-high volumes of pedestrians, particularly on transit blocks, requiring 6-8’ of pedestrian clear space that must not be encroached upon by objects such as street furniture, poles, A-frame signs, and sidewalk cafes. Minimize curb cuts and driveways to maximize pedestrian safety by reducing conflict points (See Seattle Land Use Code Section F for more information on curb cuts and driveways). Pedestrian lighting (see Downtown Design Standards) is required on Downtown Streets. |
|
Bicycle |
Protected bike facilities or in-street, minor separation, on streets with BMP recommendations. |
|
Freight |
Downtown Traffic Control Zone – freight restrictions in place for many downtown streets. |
|
Transit |
Frequent transit service on many downtown neighborhood streets; connections to light rail service. |
|
Curb Lane/Flex Zone |
Where present, alleys shall serve primary loading and parking access needs. Passenger load zones should be located at entrances of businesses, hotels and at apartment buildings (that do not have on-site facilities). Short-term storage must be balanced with providing curb space for amenity and activation. |
*Color for illustration is used to differentiate between right-of-way elements and does not represent standard color for design.